Indica qual è r e qual è s.
Quindi traccia (con un tratto più spesso) gli insiemi A =

| Sul sistema di riferimento a lato sono parzialmente tracciate le rette
r = Indica qual è r e qual è s. Quindi traccia (con un tratto più spesso) gli insiemi A = |
 |
| Per commenti: 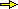 figure 2 neGli Oggetti Matematici
figure 2 neGli Oggetti Matematici# Come Ŕ stata fatta la figura con R (vedi) source("http://macosa.dima.unige.it/r.R") # se non giÓ caricato BF=3; HF=3 f = function(x) -x+3; g = function(x) 2*x-1 PLANE(0,3.2, -1,2.2) graph1(f, -1,4, "brown"); graph1(g, -1,4, "brown") # graph(f, 1,3, "seagreen"); graph(g, 1,10, "red") text(1.7,1.9, cex=0.8,"A") text(1.8,0.8, cex=0.8,"B") text(2.65,0.65, cex=0.9,font=2,"r") text(0.65,0.7, cex=0.9,font=2,"s") |
 |
| La figura con WolframAlpha: line (1,2*1-1), (3,2*3-1); segment line (1,-1+3), (3,-3+3); line (1,0),(1,1) |  |